Heat pumps have gained immense popularity as an efficient and eco-friendly solution for heating and cooling homes. One of the most common questions homeowners have about heat pumps is their lifespan: how long do Heat Pumps last, and what factors influence their longevity?
In this article, we will explore the typical lifespan of heat pumps, the factors that affect their durability, and tips for maximizing their service life.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Lifespan of a Heat Pump
Typical Heat Pump Lifespan
A heat pump’s lifespan can vary significantly, typically ranging from 10 to 20 years. Several factors influence this range, including usage patterns, maintenance practices, and quality of installation.
Local climate conditions can also play a crucial role in determining the average lifespan of a heat pump. By understanding these factors, homeowners can take steps to extend the life of their heat pump and maximize its efficiency.
Lifespan by Heat Pump Type
Air-Source Heat Pumps
Air-source heat pumps are a common type of heating and cooling system that rely on ambient air to transfer heat. While these systems can last 12 to 15 years on average, their lifespan can be significantly impacted by factors such as extreme climates and wear and tear.
Geothermal (Ground-Source) Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps are known for their exceptional longevity. These systems typically last between 20 to 25 years, with their internal components often exceeding 50 years. This remarkable durability is attributed to the stable underground temperature that provides a consistent source for heat exchange through underground loops.
Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pumps
Ductless mini-split heat pumps are smaller, versatile units that can typically last 10 to 15 years with proper installation and maintenance. These systems are comparable to air-source systems in terms of longevity, but their smaller, individual units can be more susceptible to wear and tear over time.
Water-Source Heat Pumps
Water-source heat pumps are a commonly used option for both commercial and large residential buildings. They harness the consistent water temperatures found underground or in bodies of water to heat and cool homes.
This benefit of stable temperatures reduces the stress on the system, leading to a longer lifespan. While their lifespan can vary, they often last between 15 and 20 years.

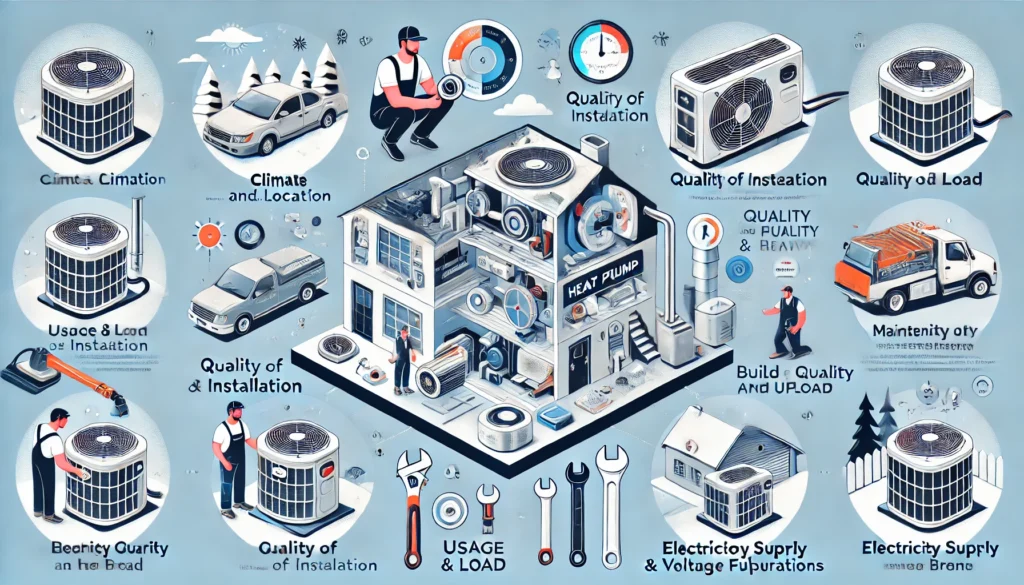
Key Factors Affecting Heat Pump Lifespan
1. Climate and Location
Climate and Location are paramount in determining a heat pump’s longevity. Air-source heat pumps, in particular, are susceptible to extreme climates. Temperature extremes can place higher strain on the system, leading to frequent defrost cycles and accelerated wear. In milder climates, heat pumps operate under less taxing conditions, extending their year-round lifespan.
2. Quality of Installation
Proper installation is paramount in ensuring a heat pump’s longevity. A missized or improperly positioned unit can lead to premature issues and significantly reduce its lifespan. Professional calibration is crucial to optimize the system’s performance and energy efficiency.
By entrusting the installation to qualified technicians, homeowners can guarantee optimal operation and extend the life of their heat pump.
3. Usage and Load
Frequent and heavy usage of a heat pump can significantly impact its life. When systems are continuously operating to meet high energy demands for heating or cooling, components experience faster wear and tear. This can lead to reduced efficiency, decreased performance, and ultimately, a shorter lifespan.
4. Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular maintenance is crucial to extending your heat pump’s life. Neglecting this can lead to early failures. Cleaning filters regularly, checking refrigerant levels, and inspecting components for wear and tear are essential steps. By prioritizing these tasks, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your heat pump.
5. Build Quality and Brand
When it comes to extending the lifespan of your heat pump, the brand and model you choose play a pivotal role. Premium manufacturers invest in durable systems equipped with higher-quality components that are designed to withstand wear and tear.
These units often come with robust warranties and superior customer support, ensuring longevity and peace of mind. While budget models may seem appealing, they might compromise on build quality and durability, potentially leading to shorter lifespans.
6. Electricity Supply and Voltage Fluctuations
One of the most overlooked factors that can significantly impact the lifespan of a heat pump is the quality of the electricity supply. Inconsistent power supply and voltage fluctuations can cause premature failures of the heat pump’s electrical components.
To prevent issues, it’s crucial to ensure stable voltage by using surge protectors. These devices can help to mitigate the impact of sudden voltage spikes and dips, thereby safeguarding the delicate electrical components of your heat pump.
Signs Your Heat Pump May Be Nearing the End of Its Lifespan
Increased Energy Bills and Frequent Repairs can be significant indicators of aging components in a heat pump. As older systems inevitably lose efficiency, they begin consuming more power to deliver the same level of heating or cooling. This can lead to a noticeable spike in your monthly utility costs.
Moreover, repeated breakdowns and costly repairs can further strain your budget and signal that your heat pump is approaching the end of its lifespan.
Additionally, Uneven Heating or Cooling and Difficulty maintaining consistent temperatures could suggest a failing heat pump. These issues often arise from refrigerant leaks, a costly issue that frequently signals the end-of-life for a heat pump.
Strange Noises, such as grinding or squealing, may indicate mechanical wear or motor failure, further exacerbating the problem.

How to Extend the Life of Your Heat Pump
1. Schedule Regular Maintenance
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your heat pump, regular maintenance is paramount. Scheduling routine check-ups with a qualified technician is essential. These inspections will identify and address potential issues such as leaks in the system, blockages in the ducts, and worn-out air filters.
By addressing these problems promptly, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your heat pump, reduce energy consumption, and maintain a comfortable indoor environment year-round.
2. Optimize Usage
One of the most effective ways to extend the life of your heat pump is to optimize its usage. By making a few simple adjustments to your thermostat settings, you can significantly reduce the strain on your system.
3. Protect Against External Elements
To ensure your heat pump operates efficiently and lasts longer, it’s crucial to shield the outdoor unit from the elements. Regularly inspect the unit for debris like leaves, twigs, and dirt, which can hinder airflow and reduce performance.
Additionally, consider using a protective cover to safeguard the unit from harsh weather conditions like rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. Proper placement of the unit is also key. Avoid positioning it in areas with obstructions that can restrict airflow, such as fences, walls, or dense vegetation.
4. Address Issues Promptly
Neglecting minor problems can quickly escalate into major repairs. Pay close attention to any unusual noises emanating from your heat pump. These sounds could signal underlying issues that, if left unchecked, can significantly reduce efficiency. Promptly addressing these concerns can save you both time and money in the long run.
5. Ensure Proper Installation
A well-installed heat pump is crucial for its longevity and efficient operation. Certified HVAC professionals should handle the installation process, ensuring the system is sized correctly to match your home’s size and climate requirements. Improper installation can lead to reduced efficiency, frequent breakdowns, and higher energy costs.
Check similar Guide: How Much Will a Heat Pump Increase My Electric Bill?
Conclusion
The lifespan of heat pumps depends on the type, quality, and level of maintenance, with averages ranging from 10 to 25 years. A long-term investment, these systems deliver consistent comfort and are highly energy-efficient, making them an ideal choice for homeowners.
Proper care and adherence to best practices can maximize their durability, ensuring that your heat pump provides reliable service for years to come. Regular servicing by a professional helps identify potential issues early, allowing you to weigh replacement options or repairs based on your budget and needs.
With thoughtful planning and routine upkeep, you can extend the life of your system, maintaining its efficiency until the end of its natural lifespan.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average lifespan of a heat pump?
The average lifespan of a heat pump ranges from 10 to 20 years. Air-source heat pumps typically last 12 to 15 years, while geothermal systems can last 20 to 25 years or more. Regular maintenance significantly affects how long a heat pump will operate efficiently.
Do different types of heat pumps have different lifespans?
Yes, the lifespan varies by type. Air-source heat pumps generally last 12 to 15 years, geothermal systems can exceed 20 years, and ductless mini-splits last 10 to 15 years. Ground loops in geothermal systems can last up to 50 years.
What factors can shorten the life of a heat pump?
Factors such as improper installation, lack of maintenance, extreme climate conditions, frequent overuse, and poor-quality components can all shorten the life of a heat pump.
How does climate affect a heat pump’s lifespan?
Extreme climates can stress heat pumps, especially air-source systems. In colder regions, the need for defrost cycles and handling freezing temperatures can reduce their lifespan. Conversely, milder climates are less taxing on the system.
Can regular maintenance extend a heat pump’s lifespan?
Yes, routine maintenance, including cleaning filters, inspecting refrigerant levels, and checking for mechanical wear, can greatly extend the lifespan of a heat pump and keep it running efficiently.
What are the signs that a heat pump is failing?
Signs of a failing heat pump include increased energy bills, uneven heating or cooling, frequent repairs, unusual noises, and difficulty maintaining consistent temperatures.
Should I repair or replace my heat pump?
If your heat pump is over 10 to 15 years old and requires frequent or costly repairs, replacement is often more cost-effective. For newer systems with minor issues, repairs may suffice.
Does brand quality impact how long a heat pump lasts?
Yes, reputable brands typically use higher-quality materials and components, resulting in longer-lasting systems. Investing in a premium brand can pay off in durability and efficiency over time.
How often should I schedule professional maintenance for my heat pump?
Professional maintenance should be scheduled annually. For systems used heavily throughout the year, consider twice-yearly check-ups to ensure optimal performance.
Do heat pumps lose efficiency as they age?
Yes, as heat pumps age, components wear out, causing efficiency to decline. Regular maintenance can slow this process, but after 10 to 15 years, noticeable efficiency losses are common.
Can a heat pump last more than 20 years?
Some heat pumps, especially geothermal systems, can last over 20 years with proper care. Regular maintenance, moderate usage, and favorable climate conditions contribute to such longevity.
What is the role of proper installation in a heat pump’s lifespan?
Proper installation ensures the system operates efficiently and reduces wear and tear. Incorrect sizing or placement can lead to inefficiency, increased strain, and a shorter lifespan.
Are geothermal heat pumps more durable than air-source systems?
Yes, geothermal heat pumps are generally more durable due to the stable underground temperature used for heat exchange. Their underground loops can last up to 50 years, far exceeding air-source systems.
How can I protect my outdoor heat pump unit?
You can protect the outdoor unit by keeping it clean, clearing debris, and ensuring proper drainage. In colder climates, consider a cover or wind barrier to shield it from harsh weather conditions.
What is the cost of replacing a heat pump?
The cost of replacing a heat pump depends on the system type, size, and brand. On average, replacement costs range from $4,000 to $10,000. Geothermal systems can be more expensive due to installation requirements.








